| Home | Concepts | API | Samples | |
| Concepts > Rasters | |||||||||||||
| Basic Principles | |||||||||||||
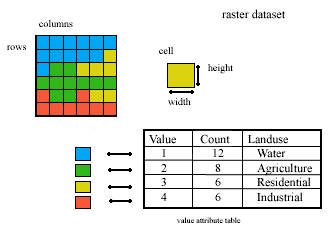
Values stored in a raster either represent discrete or continuous data. Discrete raster data represent geographic features that have definable boundaries. Discrete geographic features include buildings, wells, and land parcels. Continuous raster data represent geographic information that can vary at every location, like elevation, temperature, or radio signal strength. Continuous geographic phenomenon do not have distinct boundaries. With raster data, each pixel is independent of the other pixels, recording information only about the area it covers. For example, a pixel does not know that the pixel beside it might be part of the same tree or building. A raster is sometimes also called a scan line. A raster image, therefore, is an image made of such scan lines. See also
|
|||||||||||||
| feedback |
privacy |
legal |